Radiology
An Audiometry Lab is a specialized facility designed for the evaluation and assessment of hearing function in individuals. This controlled environment allows audiologists, hearing specialists, and healthcare professionals to conduct a variety of hearing tests and assessments to diagnose hearing disorders, determine the extent of hearing loss, and formulate appropriate interventions.
The primary equipment in an Audiometry Lab includes audiometers, which are specialized devices used to measure an individual’s hearing thresholds across different frequencies. These tests help audiologists identify the softest sounds a person can hear, providing valuable information about the type and degree of hearing loss. Pure-tone audiometry is a common test conducted in the lab, involving the presentation of tones at various frequencies and intensities.
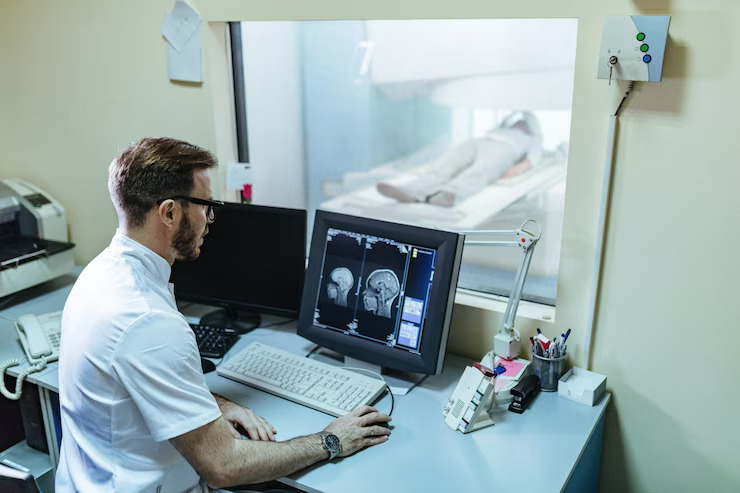
Radiology is a medical specialty that employs imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases and injuries within the human body. Radiologists, medical professionals specialized in this field, utilize various imaging modalities to obtain detailed images of internal structures, enabling them to make accurate diagnoses and guide medical interventions.
One of the foundational modalities in radiology is X-ray imaging. X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate body tissues to create images of bones and internal organs. X-rays are commonly used to detect fractures, assess joint conditions, and identify abnormalities in the chest, abdomen, and other anatomical regions.
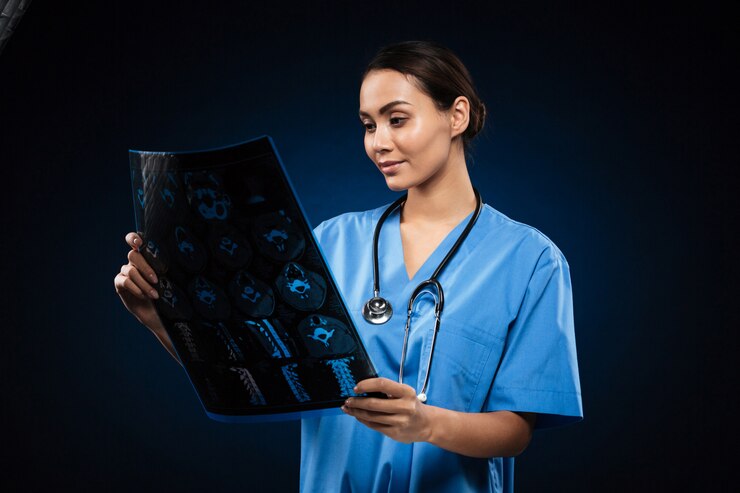

Computed Tomography (CT) is another powerful imaging technique in radiology. CT scans involve the use of X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. CT is particularly useful in visualizing soft tissues, blood vessels, and abnormalities in various organs. It is often employed for the diagnosis of conditions such as tumors, vascular diseases, and traumatic injuries.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) utilizes powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues, organs, and the musculoskeletal system. MRI is especially valuable for imaging the brain, spinal cord, joints, and organs like the liver and kidneys. It provides excellent contrast resolution, aiding in the detection and characterization of diverse medical conditions.
Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging modality that uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of internal structures. It is commonly employed in obstetrics for monitoring fetal development but is also used to visualize organs such as the heart, liver, and kidneys. Additionally, ultrasound-guided procedures are performed for interventions such as biopsies or drainage.
Nuclear Medicine is a specialized branch of radiology that involves the use of radioactive substances to diagnose and treat diseases. In nuclear imaging, patients are administered a small amount of radioactive material, and a gamma camera captures the emitted radiation to create images. This modality is often employed in the evaluation of certain cancers, cardiac conditions, and bone disorders.
Interventional Radiology is a subspecialty that involves using imaging guidance to perform minimally invasive procedures. Radiologists can, for example, use fluoroscopy or CT to guide catheters and instruments for treatments like angioplasty, embolization, or drainage procedures.
Radiology plays a pivotal role in modern medicine, providing essential diagnostic information that informs clinical decision-making. Radiologists work closely with other healthcare professionals to interpret images, contribute to treatment planning, and monitor the progress of interventions. The continual evolution of imaging technology ensures that radiology remains at the forefront of medical advancements, facilitating precise and effective patient care.
